| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Amino Acids
Analysis by HPLC |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
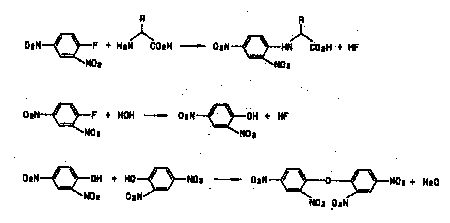
- Introduction
A convenient derivatization method of amino acids with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
as reaction reagent and a separation system were described. The
derivative amino acids were separated on a common chemically bonded
phase column with a simple linear gradient elution consisting
of aqueous buffer and methanol. The eluate was detected by common
ultraviolet absorption detector at 360 nm. The detection limits
of amino acids were as low as 10 picomole. This method has been
successfully applied to assay amino acid injection liquor used
in hospital. It has good reproducibility and precision. The procedures
avoid the requirements of particular derivative equipment and
analyzer employed in conventional amino acid analysis.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Derivatization
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Elution
Programme
| Time
(min) |
0 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
| A (%) |
70 |
50 |
45 |
35 |
30 |
10 |
70 |
A:
0.06 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 6.45) containing 0.5% organic
modifier
B: Methanol
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|